Artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to revolutionize the healthcare industry, transforming various aspects of patient care, research, and drug development. This article explores the potential applications and benefits of AI in healthcare, including streamlining workflows, enhancing diagnostic accuracy, personalizing treatment plans, and improving doctor-patient communication.
The integration of AI-powered tools, such as speech recognition, natural language processing, and machine learning algorithms, can automate time-consuming tasks, assist in early disease detection, and provide personalized treatment recommendations based on patient data. Moreover, AI’s multilingual capabilities and the increasing affordability of advanced systems are set to bridge healthcare gaps and improve access to quality care in underserved populations.
Beyond clinical care, AI is accelerating medical research and drug development by rapidly analyzing vast biomedical datasets, generating new hypotheses, and aiding in drug design. However, implementing AI in healthcare also presents challenges, such as ensuring algorithmic accuracy, addressing data privacy concerns, and building trust among patients and healthcare providers.
A collaborative approach involving healthcare professionals, technology developers, researchers, and policymakers is crucial for the responsible development and deployment of AI in healthcare. As the AI revolution in healthcare unfolds, medical professionals need to embrace this transformation, educate themselves on the capabilities and limitations of AI, and advocate for its ethical and responsible implementation to harness its full potential in improving patient outcomes and advancing the practice of medicine.
AI Is About To Transform Healthcare.
This is not a distant dream; it is an emerging reality.
Imagine this: Your patient, Mrs. Jones, walks into your office. Before she even sits down, your AI-powered tablet has pulled up her complete medical history, analyzed it, and highlighted the most relevant information for today’s visit. Much of that information is instantly downloaded from Ms. Jones’s smartwatch and health ring, which continuously monitors her health data in real time.
As you chat with Mrs. Jones, the AI listens in by using advanced speech recognition technology to transcribe your conversation accurately and in real time. By understanding the context and content of your discussion, it suggests pertinent follow-up questions you might ask. Due to the enhanced accuracy of your working diagnosis, AI suggests fewer tests to nail the diagnosis and propose temporary treatment after scanning the literature for up-to-date management.
With a wealth of data and insights at your fingertips, you can focus on what matters most: connecting with your patient and providing the best possible care. This not only enhances your efficiency but also improves the overall patient experience by ensuring that all relevant information is considered during the consultation.
This is the future of medicine that artificial intelligence is bringing to life. AI has the potential to completely transform healthcare as we know it. It is imperative that we as medical professionals understand this technology and how it will change the way we practice. In this article, as well as others to come in a future series, we’ll examine some of the most fascinating and significant uses of AI in medicine, along with the implications for you, your patients, and the delivery of healthcare in general.
Streamlining Workflows and Enhancing Efficiency
One of the most immediate benefits of AI is its ability to automate time-consuming administrative tasks. Think of all the hours you spend reviewing charts, entering data, and dealing with paperwork. AI-powered tools can take on these burdens, freeing you up to spend more quality time with patients. For instance, in many practices, physicians walk from room to room with note-takers relying on them to document patient interactions.
However, AI-driven speech recognition and natural language processing systems can now accurately transcribe and organize these notes in real time. A real-life example is the implementation of AI scribes like the one developed by Suki (12) which listens to doctor-patient conversations and automatically generates detailed clinical notes. Such technology does ambient documentation, dictation, ICD-10, and HCC coding, and answers questions. It ensures accurate and current documentation by doing away with the need for a human note-taker and integrating smoothly with electronic health record (EHR) systems.
AI can automatically extract relevant data from a patient’s medical records and present it in an easily digestible format. No more sifting through pages of notes to find that one key detail. AI can also assist with tasks like coding visits for billing, scheduling appointments, and processing prior authorizations. By streamlining your workflows, AI can help you be more productive and efficient and spend more time with the patients.
Improving Diagnostic Accuracy
AI is also poised to make a meaningful change when it comes to diagnosing. Machine-learning algorithms can be trained on lots of data, ranging from medical images and test results to the outcomes of different patients. They can recognize the subtle patterns that escape human eyes, which can lead to much earlier and more exact diagnoses. Next, are a few examples of AI applications in Radiology and Dermatology.
Dr Ronald M. Summers MD, PhD at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Clinical Center had demonstrated that machine-learning-based technology helps at making accurate diagnoses by automating detection. These systems acquire complex patterns in medical imaging and give diagnostic suggestions with similar accuracy to experienced radiologists. These applications can be used for the early detection of cancers and other critical diseases. [13]
At Clearview Health, a new study compares AI interpretation of imaging studies with that of radiologists and other physicians. The AI consistently matched or beat radiologists, and had been consistent when assisting physicians. All physicians aided by AI interpret X-rays more accurately.
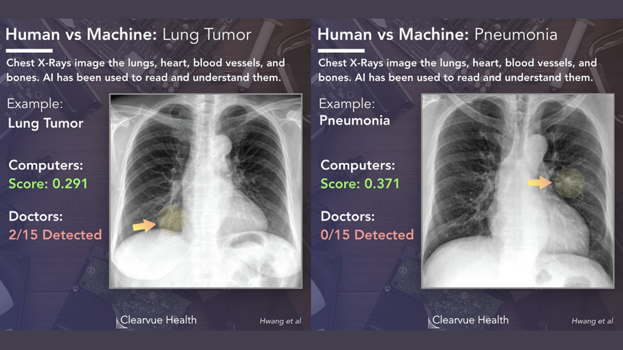
In dermatology, AI-powered tools can already outperform dermatologists at classifying skin lesions and detecting melanomas. In radiology, AI can pinpoint tiny nodules on lung CT scans, catching cancers in their earliest stages. With AI at your side, you will diagnose diseases much earlier and with higher accuracy.
Personalizing Treatment Plans
No two patients are alike, and AI will help us tailor treatments to each individual’s unique needs. By analyzing a patient’s genetic profile, medical history, and lifestyle factors, AI algorithms can predict how they will respond to different therapies. This enables us to create highly personalized treatment plans.
Imagine being able to tell a patient with hypertension, “Based on an analysis of patients with similar characteristics to you, this specific combination of medications, along with these lifestyle changes, is most likely to get your blood pressure under control.” The power of AI to personalize care will lead to better outcomes and a more satisfying experience for patients.
Enhancing Doctor-Patient Communication
AI can also help bridge gaps in doctor-patient communication. For patients, intelligent chatbots and virtual assistants can provide immediate answers to usual questions, triage concerns, and even offer basic medical advice. This frees up more of your time to focus on complex cases that require a human touch.
Smartphones Apps like “MyChart” found at Apple Store or Play Store can be enhanced to be an interactive communication tool where the patient can ask questions and have pertinent answers tailored to his or her individual set of data. Already, “MyChart” provides online access to one’s medical record, allowing the patient to view test results, medications, immunization history, and other health information. The app allows the patient to view upcoming appointments, access visit summaries with clinical notes, and even get price estimates for the cost of care.
For doctors, AI-powered tools can help ensure critical information doesn’t slip through the cracks. Imagine an AI assistant that listens in on your patient conversations, transcribes the key points, and adds them to the medical record. It could also prompt you to ask important follow-up questions and even suggest patient education materials relevant to the discussion. By enhancing communication on both sides, AI can help build stronger doctor-patient relationships.
Multilingual Capabilities and Accessibility
The multilingual capabilities of large language models (LLMs) are making healthcare more accessible worldwide. When coupled with enhanced communication tools, these models can provide medical assistance in multiple languages, breaking down language barriers and enabling better communication between first world healthcare providers and patients from diverse backgrounds in their native tongues.
As computing power becomes cheaper, the deployment of these advanced AI systems will become feasible even in resource-limited settings, improving access to quality healthcare regardless of income or location. Coupled that with Telemedicine where practitioners in the richer countries can interact with global south population and give them access to advanced medicine, with no language barrier. This democratization of healthcare is poised to bridge gaps and bring high-quality medical care to underserved populations.
Bridging the Healthcare Divide Low-Resource Settings
While AI is often associated with high-tech, well-funded healthcare systems, it also holds immense potential for improving health outcomes in low-resource settings. By leveraging the power of machine learning and mobile technologies, AI can help bridge the healthcare divide and bring quality care to underserved populations.
One promising application is using AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants to provide basic health information and triage advice. In areas with limited access to healthcare providers, these tools can be a lifeline, helping people understand their symptoms and seek appropriate care. For example, the World Health Organization (WHO) has developed a chatbot that provides information about COVID-19 and helps users self-assess their risk [1].
AI can also aid in disease surveillance and outbreak prediction in low-resource settings. By analyzing data from mobile phones, social media, and other digital sources, machine learning algorithms can detect disease patterns and predict the spread of infectious diseases [13]. This can help public health officials allocate resources more efficiently and implement targeted interventions to control outbreaks.
Additionally, AI-powered point-of-care diagnostic tools can bring significant changes in settings with limited laboratory infrastructure. For instance, researchers have developed machine learning algorithms that can analyze smartphone images to detect malaria parasites in blood samples[3]. Such tools can enable rapid, accurate diagnosis in the field, leading to earlier treatment and better outcomes.
However, implementing AI in low-resource settings also poses challenges. These include ensuring the availability of reliable digital infrastructure, addressing data privacy concerns, and adapting AI tools to local languages and cultural contexts. Collaboration between technology developers, healthcare providers, and local communities is essential to ensure that AI solutions are appropriate, acceptable, and sustainable[4].
Despite these challenges, the potential for AI to improve healthcare in low-resource settings is vast. As smartphone penetration continues to rise globally, and as AI tools become more efficient and affordable, we have an unprecedented opportunity to leverage these technologies to bridge health inequities and ensure access to quality care for all.
Advancing Research and Drug Development
Beyond transforming clinical care, AI is also accelerating the pace of medical research and drug development. Machine learning can rapidly sift through massive biomedical datasets to generate new hypotheses and identify promising drug targets. AI-powered patient recruitment tools can match eligible patients to clinical trials in minutes rather than months. And AI can even aid in designing new drugs by predicting how molecules will interact with the body.
These AI breakthroughs in research will ultimately translate into better treatments for your patients. You will have access to more effective therapies, targeted to specific disease pathways. We may even see cures for conditions once thought untreatable. By advancing the frontiers of medical knowledge, AI is ushering in a new era of possibility.
Preparing for the AI Future
The AI revolution in healthcare is no longer a distant dream—it’s happening now. As physicians, we must embrace this transformation and prepare ourselves to integrate AI into our practices. This means investing in education to understand the capabilities and limitations of healthcare AI. It means being open to new ways of working, with AI as our partner. And it means advocating for the responsible development and deployment of AI, always keeping the best interests of patients at the center.
The potential of AI to elevate the practice of medicine is immense. By streamlining our workflows, enhancing diagnostic accuracy, personalizing treatments, strengthening communication, and accelerating research, AI will enable us to provide better care to more patients. It will augment our capabilities, but not replace our vital role. The doctor-patient relationship remains at the heart of healthcare.
Challenges and Considerations
While promising, the integration of AI in healthcare poses challenges, including ensuring the accuracy and reliability of AI algorithms, addressing data privacy and security concerns, and building trust among patients and healthcare providers.
To fully realize the potential of AI in healthcare, a multi-faceted approach is needed, involving collaboration between healthcare providers, technology companies, researchers, and policymakers. This includes adopting risk-based approaches, investing in research and development, strengthening consumer trust, and implementing appropriate governance and oversight mechanisms.
For more information or to discuss ways to integrate AI in your healthcare practice, please contact the authors.
Conclusion: Harnessing the Power of AI for Better Healthcare
AI is set to revolutionize healthcare, offering a myriad of benefits from streamlining workflows and enhancing diagnostic accuracy to personalizing treatment plans and improving doctor-patient communication. As we have explored in this introductory article, AI has the potential to transform the way we practice medicine, ultimately leading to better health outcomes for patients.
However, the integration of AI in healthcare also presents challenges that must be addressed, including ensuring the accuracy and reliability of AI algorithms, safeguarding data privacy and security, and building trust among patients and healthcare providers. A collaborative approach involving all stakeholders is essential to realize the full potential of AI in healthcare.
This article marks the beginning of a series delving into the transformative power of AI in healthcare. Upcoming articles will explore ethical considerations, the impact on the healthcare workforce, patient perspectives, and regulatory and policy implications. As healthcare professionals, it is our responsibility to embrace this transformation, educate ourselves on the capabilities and limitations of AI, and advocate for its responsible implementation.
The AI revolution in healthcare is underway, and by harnessing its power, we can elevate the practice of medicine and provide better care to more patients. As we navigate this exciting new frontier, we must approach the integration of AI with care, always prioritizing the best interests of those we serve.
References
- World Health Organization. (2022). WHO Health Alert brings COVID-19 facts to billions via WhatsApp. https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/who-health-alert-brings-covid-19-facts-to-billions-via-whatsapp
- Whitelaw, S., Mamas, M. A., Topol, E., & Van Spall, H. G. (2020). Applications of digital technology in COVID-19 pandemic planning and response. The Lancet Digital Health, 2(8), e435-e440.
- Cunningham, J. A., Bondy, S. J., & Lynskey, M. T. (2021). Machine learning in the prediction of infectious disease spread: A systematic review. Journal of Global Health, 11, 04037.
- Wahl, B., Cossy-Gantner, A., Germann, S., & Schwalbe, N. R. (2018). Artificial intelligence (AI) and global health: How can AI contribute to health in resource-poor settings? BMJ Global Health, 3(4), e000798.
- Bibault, J. E., Chaix, B., & Nectoux, P. (2021). Artificial intelligence for triage in primary care: A review. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 23(4), e25199.
- Esteva, A., Chou, K., Yeung, S., Naik, N., Madani, A., & Mottaghi, R. (2021). Deep learning for healthcare: A review. Nature Medicine, 27(1), 25-36.
- Chaudhari, R., Fong, L. W., & Tan, Z. (2020). Artificial intelligence in drug discovery and development. Drug Discovery Today, 25(7), 1193-1201.
- Holzinger, A., Biemann, C., Pattichis, C. S., & Kell, D. B. (2019). What do we need to build explainable AI systems for the medical domain? arXiv preprint arXiv :1712.09923.
- Obermeyer, Z., Powers, B., Vogeli, C., & Mullainathan, S. (2019). Dissecting racial bias in an algorithm used to manage the health of populations. Science, 366(6464), 447-453.
- AI Revolution in Medicine: GPT-4 and Beyond. (2024). Amazon https://www.amazon.com/AI-Revolution-Medicine-GPT-4-Beyond/dp/0138200130
- Syneos Health Podcast: 2024 Health Trends – Managing the Healthcare Revolution. Syneos Health.
- https://www.suki.ai/
13 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22465077/

